Deforestation, land grabbing, and human and labour rights violations have been associated with the production of natural rubber. In order to transform the global natural rubber supply chain into a fair, equitable and environmentally sound one, it is crucial that we work to reduce such social and environmental risks. This is by no means an easy feat with about 6 million smallholder farmers producing around 85% of the world’s natural rubber; the complexities of the supply chain make it difficult for buyers to ensure that sustainable practices are employed for rubber cultivation and processing. Recognizing the importance of enhancing traceability and transparency in the natural rubber supply chain to support the identification and mitigation of social and environmental risks, GPSNR established the Traceability and Transparency Working Group.
Over the past few months, the Working Group has commissioned two studies around traceability and transparency tools and technology. The reports were submitted by the consultants at the end of October 2020. The findings from each report are summarized below.
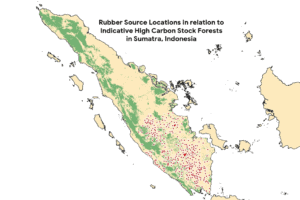
Spatial Data & Mapping Tools for Detecting Deforestation and Threats to HCVS Areas in Rubber Production Landscapes
Report developed by Zoological Society of London (ZSL)
This report reviews a variety of spatial mapping tools and approaches which may be employed by GPSNR and its members to address deforestation and degradation risk in rubber supply chains.
The key recommendations from this study are that GPSNR members should pool resources to collectively commission landscape-level HCV and HCS screening for key rubber-producing countries and these should be updated periodically. Spatial data maps from this process should be made publicly available to encourage cross-sectoral collaboration on tackling deforestation.
HCV/S datasets may then be integrated into satellite monitoring platforms and combined with near-real time monitoring of deforestation and forest degradation. This will allow accurate spatial analysis of the impacts of rubber production in key forested landscapes. GPSNR members may select different satellite monitoring tools or service providers, based on their own needs and budget. For upstream actors closer to the source, satellite monitoring may allow for preventative measures to be taken at the early stages of deforestation.
The full Executive Summary can be viewed here.
Review of Transparency & Traceability Tools and Solutions
Report prepared by e-Audit Hong-Kong Ltd
This report presents options on supply chain transparency and/ or product traceability solutions that GPSNR may consider as well as recommendations to select the most suitable transparency/traceability solutions for the GPSNR initiative.
A range of solutions currently implemented in commodity industries similar to the natural rubber industry were reviewed and evaluated, resulting in the identification of several key elements that will need to be considered to select the most suitable and cost-efficient solution.
The report also considers three potential infrastructure options (centralized, hybrid and decentralized) that should be considered as they have profound implications on the range of supply chain transparency and product/batch traceability solution(s) that GPSNR may consider to adopt.
This report concludes that the technology currently available makes it possible for all GPSNR key requirements to be integrated into one single solution. However, such a centralized solution may be costly and cumbersome to implement. At this stage of development of the GPSNR initiative it is recommended that GPSNR starts implementing a more flexible hybrid solution, with a centralized infrastructure/ data hub focused on reporting and monitoring of clearly defined performance KPIs, that can be connected through APIs to existing field level risk assessment, risk mapping and traceability solutions currently implemented by GPSNR members.
The full Executive Summary can be viewed here.